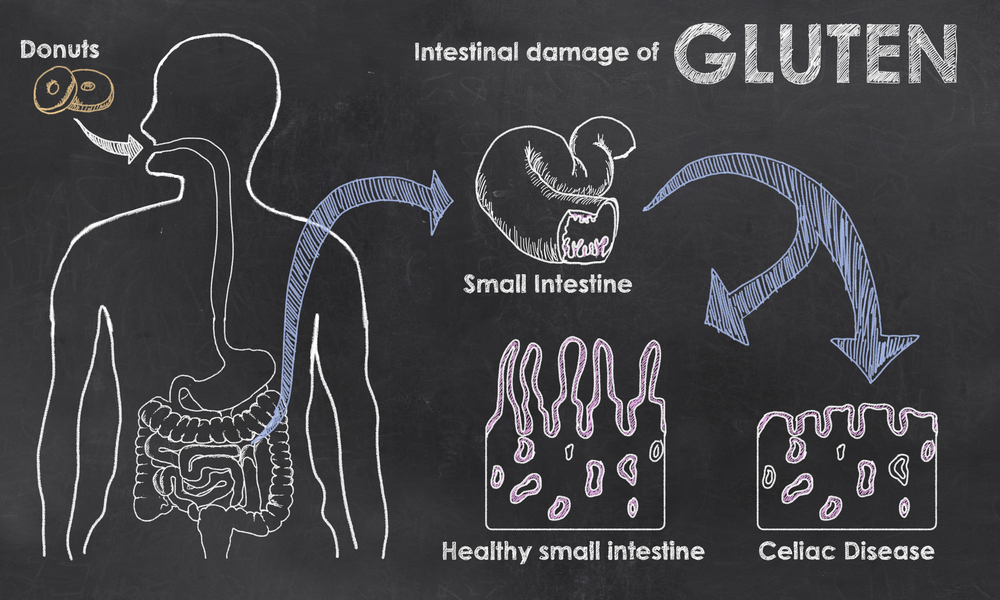
Celiac disease is a chronic disorder. It affects your digestive system, and damages your small intestines. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that has a reaction when you eat gluten. Gluten triggers an immune response in the small intestines. This reaction can damage the lining of the small intestines. This damage can stop the small intestines from absorbing the nutrients you need from your food.
One in 100 people may have celiac disease. Only about 30% of the people who have it will be diagnosed appropriately. If celiac disease is left untreated it can cause serious long term health problems.
Risks & Possible Causes of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease seems to be genetic. If you have a person in your family who has it you have a greater risk of having it yourself. Some people who have someone in their family won’t get celiac disease, while people who have no hereditary markers will develop the disease overtime.
Some believe that this disease may be triggered by a significant physical stress that overextends the immune system. This could be a surgery, illness, or pregnancy.
Other studies say the disease could be triggered by microorganisms in your gut.
You have a higher risk of developing celiac disease if you have someone in your family who has it, if you have another autoimmune condition, if you have a chromosomal disorder, or if you are female.
Celiac disease can develop at any age, but there are two common windows of when it is normally diagnosed. The first one being between 8-12 months old, usually after children start to eat solid foods and may become in contact with gluten. The other window is later on in life between 40-60 years old.
Types Of Celiac Disease
Non-Responsive Celiac Disease
There is non-responsive celiac disease which is when the symptoms of the disease do not stop with a gluten free diet. This can be for a number of reasons. The first being that your food is being contaminated with gluten. A dietician will be able to help you have the best knowledge to know how to go 100% gluten free in your diet.
Other causes of non-responsive celiac disease are bacterial overgrowth in the small intestines, microscopic colitis, pancreatic insufficiency, irritable bowel syndrome, difficulty digesting lactose, sucrose, or fructose.
Refractory Celiac Disease
In some instances you may have refractory celiac disease which is when the intestinal injury doesn’t respond to a gluten free diet at all. You may still have symptoms after being 100% gluten free after 6 months to a year.
Symptoms Of Celiac Disease
Symptoms of this condition vary from person to person. You may only experience some of the symptoms or you may have all of them. Symptoms can also range in severity.
With celiac disease the most common symptoms are in the digestive tract. Symptoms include diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating, gas, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
Symptoms that are not related to the digestive tract are anemia, osteoporosis, dermatitis herpetiformis, mouth ulcers, headaches, fatigue, tingling in feet and hands, joint pain, hyposplenism, elevated liver enzymes, abnormal periods, and mood changes.
Diagnosing Celiac Disease
There are two different ways your doctor can diagnose you with celiac disease. They are usually both done to confirm the condition.
The first is a blood test. The blood test will be able to let your doctor look for the gluten antibodies in your system. Try not to be completely gluten free before you speak with your doctor, because the small intestines will start to heal and they may not be able to diagnose you appropriately.
The second test is an upper endoscopy. This is done by putting a small camera down your throat to the first part of the small intestines. Then the doctor will be able to take a biopsy to check for damage in the small intestines.
If both these tests come back and you indeed have celiac disease your doctor may want to do further testing to check for deficiencies such as iron, vitamin D, electrolyte, or calcium.
Treating Celiac Disease
The first course of treatment for celiac disease is to be 100% gluten free in your diet. Your body will never change how it reacts to gluten, but stopping eating gluten can help your body start to heal.
You may also need nutritional supplements to make sure you don’t have any deficiencies especially after first being diagnosed.
Corticosteroids can be prescribed to help lower inflammation in the body, that isn’t being lowered fast enough with an anti-inflammatory diet.
Continuous follow up will be needed with this condition, you will also have to go under further testing to make sure your celiac disease is responding to the gluten free diet. Once you have started going gluten free your small intestines should start healing and eventually will be able to absorb nutrients like it should.
If you leave your celiac disease left untreated it can cause serious complications. Some of these are malnutrition, bone weakening, infertility, miscarriages, lactose intolerance, cancer, peripheral neuropathy, gallbladder malfunction, heart disease, liver failure, and pancreatic insufficiency.
Digestion: Celiac Disease left untreated it can cause serious complications! #HealthSurgeon
READ MORE: How To Get Rid Of Gas Naturally
Sources:
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease#:~:text=Celiac%20disease%20is%20a%20chronic,all%20the%20nutrients%20it%20needs.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/celiac-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352225
https://celiac.org/about-celiac-disease/what-is-celiac-disease/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14240-celiac-disease