Magnesium is one of seven essential macronutrients your body needs. Your body cannot make magnesium on its own so you have to get it from your diet or supplements. The recommended amount of magnesium is about 100 mg per day.
When getting magnesium from your diet it is usually not harmful to eat more than this for a healthy person. Your body will just discard any excess in waste. Your body stores about 25 mg of magnesium in your bones.
When taking in supplemental form you can take too much which can lead to some adverse symptoms such as stomach pains, and vomiting.
Magnesium food sources are salmon, halibut, mackerel, spinach, swiss chard, edamame, tamarind, potato with skin, okra, quinoa, whole grains, black eyed, peas, tempeh, soy, cooked beans, almonds, cashews, flaxseed, peanut butter, tap water, and mineral waters.
Magnesium Deficiency
A magnesium deficiency is common. Many people are right on the edge of a deficiency, but may not know it. There may be no symptoms if the deficiency isn’t that great, and the person is healthy.
There are some conditions that raise the risk of a deficiency like digestive disorders, type 2 diabetes, refeeding syndrome, hungry bone syndrome, or genetic kidney problems.
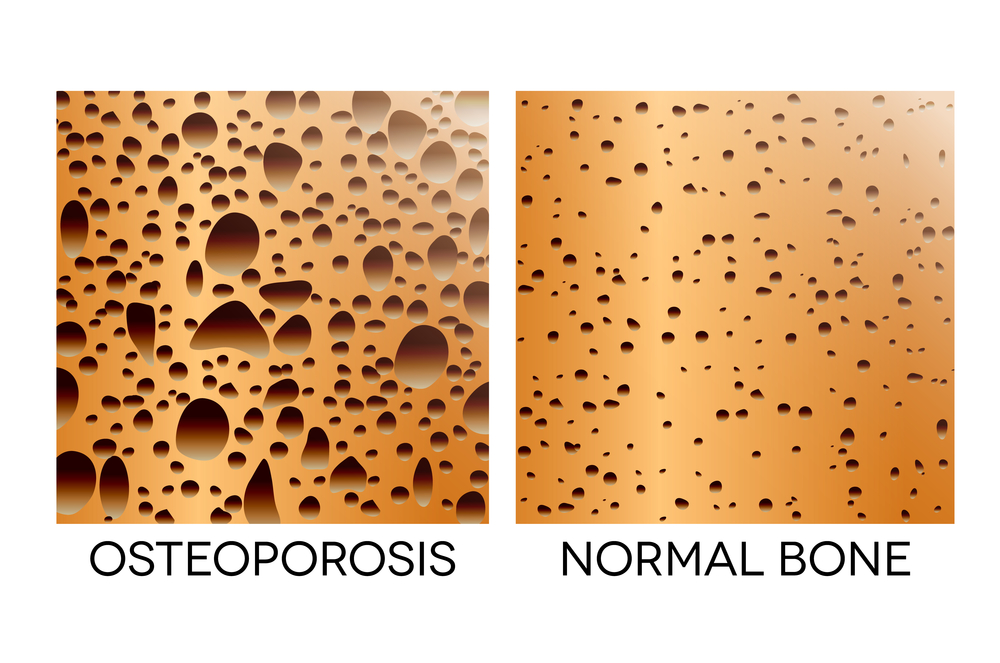
Signs and symptoms of a magnesium deficiency are loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, weakness, muscle spasms, cramps, high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, seizures, personality changes, and osteoporosis.
Increasing the amount of magnesium rich foods in your diet can help with your deficiency. Supplements may also be needed. Make sure you take the correct dosage so you don’t end up with magnesium toxicity.
What does magnesium do?
Magnesium helps with over 300 enzyme reactions in the body. It is a helper molecule that assists with energy creation, protein formation, gene maintenance, muscle movements, and nervous system regulations. It helps the immune system, as well as brain function.
Health Benefits Of Magnesium
Strengthens Muscles
Magnesium has been shown to help with exercise performance. Magnesium helps move blood sugar to the muscles and dispose of lactate from the muscles, which in return lessens fatigue while working out. Adding in magnesium may also help increase muscle mass and power.
Lowers Diabetes Risk
Magnesium is an important factor in glucose control and insulin metabolism. This is important especially for those that are at risk for type 2 diabetes, or have type 2 diabetes.
About 48% of people who have type 2 diabetes have low levels of magnesium. A deficiency of magnesium worsens insulin resistance and in return insulin resistance worsens a magnesium deficiency.
Consuming magnesium in your diet daily may lower your risk of diabetes. As well as improve your insulin resistance if you have type 2 diabetes already.
Improves Heart Health
Your heart is a muscle, magnesium helps maintain the muscles in your body so it helps with your heart health as well. Magnesium helps lower blood pressure. Which lowers your risk of heart disease and stroke.
When someone suffers a heart attack if they are given magnesium quickly after the attack they have a lower risk of mortality after.
Prevents Migraines
Magnesium may also help aid with migraines. People who have migraines usually have low levels of magnesium at the time of the migraine. A magnesium deficiency can affect the neurotransmitters and restrict blood vessel constriction, both of which are linked to causing a migraine.
Taking supplements may help keep levels of magnesium up which can help lessen the amount of migraine attacks you may have.
Improves & Maintains Bone Strength
About 50-60% of the magnesium you have in your body is in your bones. Magnesium helps prevent bone loss. When magnesium is stored in the body it is stored in the skeletal system. Having an adequate magnesium intake helps with bone density, and bone crystal formation, it also lowers the risk of osteoporosis.
Magnesium also helps regulate calcium and vitamin D which are both essential for bone health too.
Aids Quality Sleep
Magnesium may also be an all natural remedy for insomnia.
Lowers Inflammation
It also has anti-inflammatory properties which can help lower inflammation throughout the body.
Helps Your Brain & Moods
It improves brain function and moods. Low levels of magnesium have been shown to be linked with depression and anxiety.
Lessens PMS Symptoms
Magnesium levels also fluctuate during menstrual cycles, which can cause symptoms such as water retention, abdominal cramps, tiredness, and headaches. So taking a little extra magnesium may help lessen PMS symptoms.
Takeaway
Magnesium is an important macronutrient that helps over 300 enzyme reactions in the body. Your body cannot make magnesium so it is important to add magnesium rich foods into your diet.
Many people don’t take enough magnesium which can cause a deficiency. Signs and symptoms may not be noticed in a healthy person so it is important to get your levels checked if you suspect a deficiency.
Having good levels of magnesium in your body can lower your risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis.
Magnesium is a macronutrient that can help prevent migraines and reduce the risk of diabetes! Do you get enough? #HealthSurgeon
Sources:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/magnesium-supplements/faq-20466270#:~:text=Magnesium%20plays%20many%20crucial%20roles,type%202%20diabetes%20and%20osteoporosis.
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/magnesium-benefits#TOC_TITLE_HDR_2
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/286839#benefits
https://ro.co/health-guide/magnesium-deficiency-signs/
https://www.webmd.com/diet/magnesium-and-your-health