Collagen is a protein that is found in many animals, including humans. It is a structural protein that is found in tendons, ligaments, and bones. Different parts of the skin contain different amounts of collagen. The collagen protein is important for both medical and cosmetic purposes. It can be used to improve the complexion or promote bone and cartilage health.
Within the last few years, collagen has become a popular health supplement. This protein is found in animal tissues and plays an important role in maintaining the strength and structure of the skin, hair, nails, and joints. Although it is safe for most people to take, there are a few potential side effects that you should be aware of before taking collagen. These include indigestion, bloating, and constipation. If you experience any of these side effects, discontinue use and consult your doctor.
What is collagen?
Collagen is a protein found in the connective tissues of animals, including humans. It is the most abundant protein in the animal kingdom, accounting for about 25% to 35% of the total protein content. Collagen is composed of amino acids arranged in a triple-helical structure.
There are several types of collagen, all of which are characterized by their amino acid composition and the way the collagen molecules are arranged. Type I collagen, for example, is the most abundant type of collagen in the human body and is responsible for the strength and elasticity of the skin. Type II collagen is found in cartilage, while type III collagen is found in the walls of hollow organs such as the gastrointestinal tract and blood vessels.
Collagen protein can be added to the diet in a number of ways. One way is to consume foods that are rich in collagen, such as bone broth or chicken feet. Another way is to take collagen supplements, which are available in powder, pill, or liquid form.
To add collagen protein to your diet: Consume foods that are rich in collagen, such as bone broth or chicken feet.
Collagen
Collagen is one of the structural proteins in the body that serves as a scaffold in cells and tissues.
Other proteins act as enzymes, but these proteins give cells and tissues their shape and tension.
Collagen is one of the most important structural proteins in the body, along with creatine and elastin. It helps keep the structures elastic, but also ensures a certain level of strength.
Collagen Composition
The collagen always has long protein chains, the collagen molecules. These form a left-handed helix, also called a helix. Three of these structures are arranged into a so-called superhelix.
The stability of the strands is ensured by hydrogen bridges between them.
Collagen fibers are wound tightly together, giving them a high tensile strength, but they are not very stretchy.
Types of Collagen
There are different types of collagen, with type I being the most common in humans. Therefore, the term collagen is often used interchangeably with type I collagen in general usage.
As many as 28 different types of collagen are known to exist, with an additional 10 proteins having collagen-like structures.
Type I Collagen
Type I collagen is a collagen that can form fibrils. Type I mainly occurs in the following body structures:
- Bones
- Fibrocartilage
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Fascia
- Skin
- Dentin
- Leather and cornea in the eye
Type II Collagen
Type II collagen is a protein that helps to form fibers. It is found in the hyaline and elastic cartilage, as well as in the fibrous cartilage and the vitreous body of the eye.
Type III Collagen
Type III collagen is a type of collagen that is often found in conjunction with type I collagen. Like type I collagen, type III collagen is also a fiber-forming collagen that belongs to the category of fibrillary collagens.
The reticular fibers are made up of collagen III and are thus an important component of reticular connective tissue. These fibers are particularly fine strands that are arranged in a reticulated structure.
The reticular tissue is part of lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleen or tonsils and palate tonsils. But type III can also be found in the following body structures:
- Cartilage
- Dentin
- Tendons
- Bone substance
- Heart
Other Types Of Collagen
Collagen IV is a type of collagen that forms a network-like structure. It is mostly found in the basal membrane. The basal membrane is a thin layer of tissue that separates epithelial tissue from connective tissue below it.
This protein is found in the extracellular matrix of skeletal muscle, where it is associated with fibers.
There are many types of collagen, each with its own purpose. tendons, bone, cartilage, fat, and nerve tissue all contain collagen. skin also contains a type of collagen.
There are other types of collagens that form fibers and are found in the body, such as those that are part of the placenta or fetal tissue.
The purpose of many types of collagen are still unknown, but they are found in the internal organs, skin, growth areas of the cartilage, and eyes.
Collagen as a Dietary Supplement
Hydrolyzed collagen is a form of collagen that has been made water-soluble by enzymatic processes. It is mostly used in food supplements. This means that collagen hydrolyzate can be easily absorbed by the body and used effectively.
Most products that use collagen derive it from animals. Possible sources of animal-based collagen are, for example, chicken bones or fish skin. But there are also synthetic collagens that can be used as food supplements.
Collagen Peptides and Collagen Hydrolyzate
Other forms of collagen that can be found in food supplements include collagen hydrolyzate and collagen peptides.
Collagen hydrolyzate is a type of collagen that has been enzymatically modified to make it water-soluble.
Collagen peptides are hydrolyzed collagen that has been broken down into smaller pieces.
Collagen Types in Nutritional Supplements
Type I and type II collagen are the two types of collagen found in dietary supplements. Pay close attention to the type of collagen contained in the supplement you wish to purchase.
There are two types of collagen, type I and type II. Type I collagen is found mainly in the skin and bone, while type II collagen is found in cartilage.
Individuals with joint problems are more likely to use dietary supplements containing type II collagen. Those individuals who want to improve the appearance of their skin or nails would benefit from taking a type I dietary supplement.
Although the types are separated in the text, they actually appear mixed in the body.
Collagen Supplements Forms
If you don’t want to drink it, you can take the collagen in tablet or capsule form. This dosage form is particularly practical when you’re on the go or traveling.
As a result, it is easy to take. Furthermore, it is the most effective and also the most expensive way to consume collagen. Collagen hydrolyzate in powder form is mostly odorless and tasteless and can be easily dissolved in water. This makes it easy to take. Furthermore, it is the most effective and also the most expensive way to consume collagen.
Collagen in the Cosmetics Industry
Collagen is a structural protein that is found in many moisturizing and skin-tightening creams. It is particularly popular in the beauty and anti-aging industry due to its ability to firm the skin.
Collagen is a popular ingredient in many cosmetics, such as shower gel, mascara, lipstick, and after-sun lotion.
Collagen is not only found in cosmetics, but also in many hair care products. It is supposed to wrap around the hair like a film so that it appears smoother and is also easier to comb.
Tips when using Collagen Protein
Do your research before adding collagen to your diet or supplement routine, and be sure to consult your healthcare provider to ensure it is the right decision for you.
1. There are different sources and types of collagen
Collagen is a protein which is produced in the bodies of animals and is the main component of connective tissue and cartilage. It can also be found in high quantities in muscle tissue where it contributes to muscle elasticity.
Commercial collagen protein is generally from cows, although you can also from fish now too. Collagen is extracted by cooking cartilaginous animal materials like bones, connective tissue, and skin.
If you are a strict vegetarian or vegan, or if you keep kosher, then collagen protein is not for you.
2. Collagen is not a complete protein
Collagen may be a good source of protein for those who are not strict vegetarians, vegans, or kosher. It is mostly protein by volume, but it is not a complete protein.
One tablespoon of collagen contains a significant amount of protein that is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream.
3. Collagen may come from factory farms unless labeled otherwise
Beware of the source of your collagen protein.
The Consumer Wellness Center tested several brands of collagen protein and found that those not sourced from organic livestock contained concentrated animal feeding operations byproducts such as endocrine-disrupting chemicals, prescription drugs, and antibiotics.
Although the legitimacy of the studies is being contested, it’s advised that you look for collagen protein that is certified organic and raised on pasture (or grass-fed) to avoid CAFO byproducts.
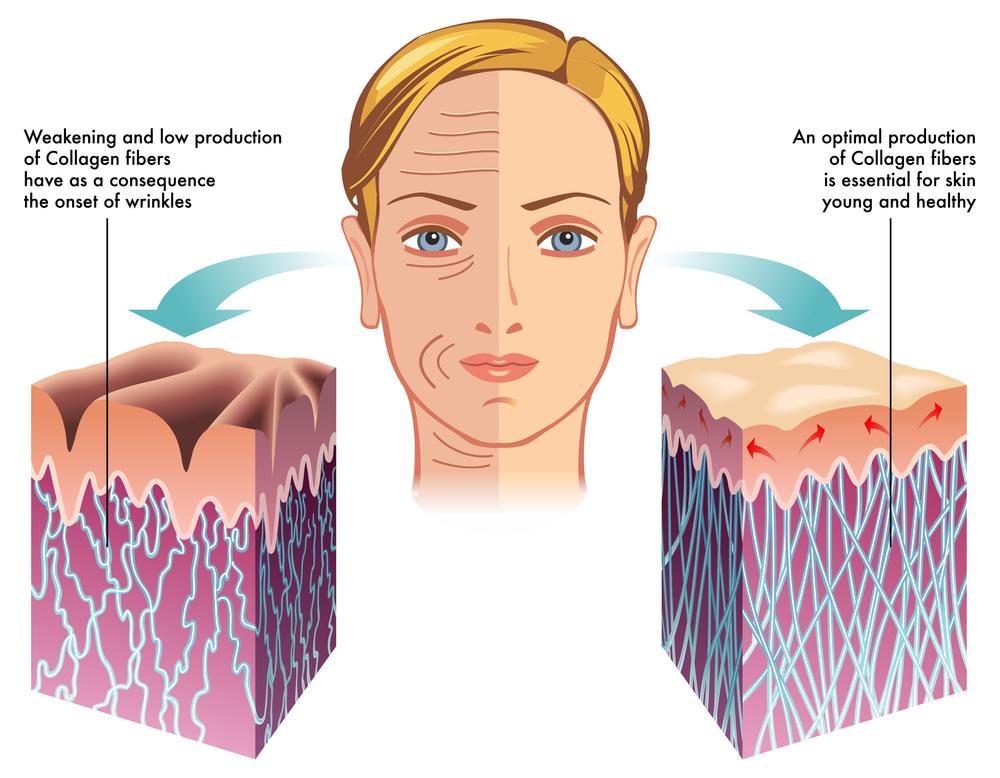
4. Collagen helps nourish skin, hair and nails, but only if ingested
While many skincare products claim to contain collagen, it is not actually possible for the skin to absorb it. This is because the collagen molecules are too large.
The most effective way to get the benefits of collagen is to consume it in your diet, as it is more easily absorbed by the body.
According to clinical studies, consuming collagen every day can significantly improve your skin’s elasticity and moisture.
When you eat collagen peptides, they may help your body create and reorganize new collagen fibers. This happens because they stimulate the fibroblasts in the connective tissues of your skin.
Many topical beauty products contain collagen, which may improve the strength of the skin, hair and nails due to the abundance of amino acids in collagen. However, the collagen molecules in these products are too large to be absorbed, so they don’t have much effect.
5. Collagen can support bone and joint health
Collagen comprises approximately 90% of our bone mass, so replenishing it through supplementation may be crucial to maintaining bone health.
Research indicates that taking collagen as a supplement can also improve joint health by easing joint pain and swelling.
The anti-inflammatory properties of the amino acids glycine and proline, found in collagen, help soothe achy or weak joints. As your joints are made of collagen, it’s important to ensure you have enough of it to keep them healthy.
The amino acids in collagen protein may help to rebuild joint cartilage and may also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
6. Collagen can support digestion and satiety
Collagen is important for a healthy intestinal lining because it makes up the villi in your intestinal lining and helps repair loose junctions in your gut.
The amino acids in collagen can help to heal the digestive tract. One of the amino acids, glycine, is found in abundance in collagen. Glycine has been shown to help produce stomach acid, which can improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
Another clinical study found that people who ate collagen protein for breakfast were up to 400% more satisfied and ate 20% less at lunch than people who ate other protein sources like soy and whey.
7. Collagen might increase histamine levels
If you have a histamine intolerance, you might have a negative reaction to collagen protein. It’s uncommon to hear about side effects from collagen protein, though.
Although some people who began taking collagen peptides said they had more histamine reactions,
8. Collagen might deplete tryptophan levels
Collagen has been shown to be effective in lowering serotonin levels in tryptophan-depletion studies. Tryptophan is a precursor to serotonin, so this makes sense.
There is a connection between serotonin and behavior. Some patients have said that they feel better when they consume collagen protein, while others have reported feeling worse.
If you are easily upset or you have problems like anxiety and depression, you should be careful about taking collagen protein powder.
9. Collagen may not work for people who are sensitive to glutamine
If you have Leaky Gut Syndrome, your doctor may recommend that you consume collagen protein. However, if you are sensitive to glutamine, you should be careful when consuming collagen protein.
It is essential for the health of immune, gastrointestinal, and muscular systems. Glutamine is an amino acid that is found in large amounts in collagen protein. It is necessary for the health of immune, gastrointestinal, and muscular systems. While glutamine is beneficial for some, others may be sensitive to it since they may suffer from a more severe case of Leaky Gut Syndrome.
If you have high levels of glutamic acid in your brain, you may experience brain fog, migraines, mood swings, more serious mood disorders, and even seizures.
10. You can get collagen from real food sources
You can increase your collagen levels through supplementation, or by consuming whole foods. Note that you may not need to supplement your diet if you’re eating a real food diet.
Collagen supplements may help improve your overall diet if you do not eat perfectly healthy. If you follow a pescatarian diet, marine collagen supplements may also help prevent deficiencies.
READ MORE: 7 Healthy Fruit and Veg Juice Recipe for Glowing Skin