Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas, specifically by the beta cells within the islets of Langerhans. Its primary function is to regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat, and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues, the glucose is either used as fuel or converted into fat for longer-term storage. Without insulin, cells would be unable to utilize glucose as energy, leading to various metabolic disruptions.
The Role of Insulin in the Body
Insulin plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s energy balance. When we consume food, particularly carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. The rise in blood glucose levels triggers the pancreas to release insulin, which facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, keeping blood sugar levels within a narrow, healthy range. Insulin also has effects on lipid and protein metabolism, inhibiting the breakdown of fat and protein, further illustrating its importance as a regulatory hormone.
Insulin Resistance and Its Implications
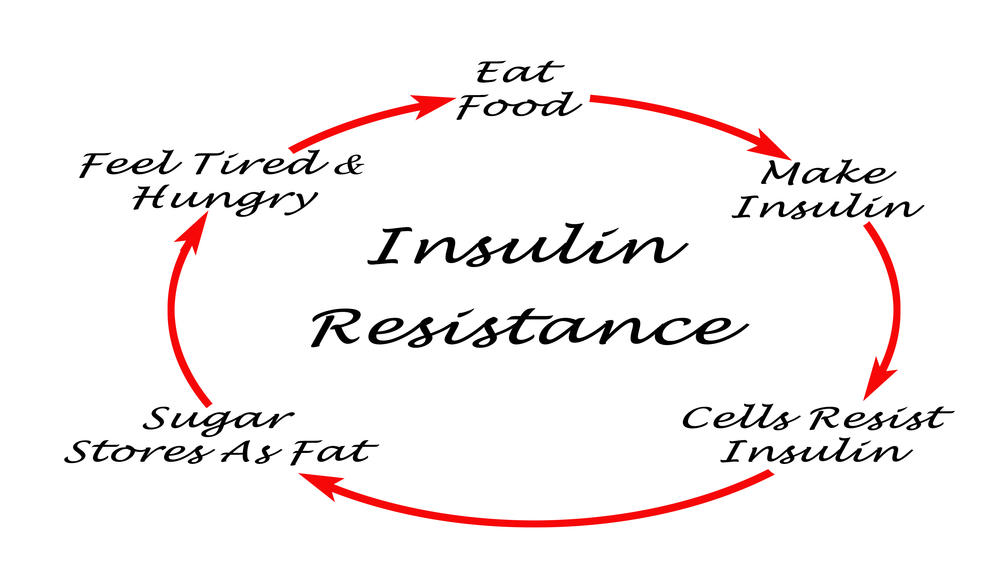
Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body do not respond effectively to insulin. This can lead to higher levels of glucose in the blood, as insulin is less able to facilitate its entry into cells. Over time, this can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative insulin deficiency. Insulin resistance is often associated with obesity and can lead to a host of health issues, including cardiovascular disease.
The Importance of Natural Insulin Regulation
Natural regulation of insulin is crucial for optimal health. The body’s ability to produce and respond to insulin effectively ensures that glucose is properly managed, providing energy to cells and maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Disruptions in this balance, such as those caused by excessive insulin production or insulin resistance, can lead to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, respectively. Both conditions can have serious health consequences if not managed properly. Therefore, understanding and supporting the body’s natural insulin regulation is essential for preventing metabolic diseases and maintaining overall health.
Dietary Influences on Insulin Production
Macronutrients and Their Effects on Insulin
Macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play a significant role in insulin production and regulation. Carbohydrates have the most immediate impact on insulin levels due to their effect on blood glucose. Simple carbohydrates, such as sugars, cause rapid spikes in insulin secretion, while complex carbohydrates, like those found in whole grains, result in a slower, more controlled insulin response. Proteins can also stimulate insulin release, but to a lesser extent than carbohydrates. High protein diets, particularly those rich in amino acids, can modulate glucose homeostasis and have an insulinotropic effect. Fats have minimal direct impact on insulin secretion but can influence insulin sensitivity, especially when consumed in large amounts as part of a high-calorie diet.
The Impact of Processed Foods on Insulin Sensitivity
Processed foods, which are often high in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats, can detrimentally affect insulin sensitivity. Regular consumption of these foods can lead to chronic hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, and eventually type 2 diabetes. Processed foods also tend to be low in fiber and nutrients, further exacerbating their negative impact on insulin regulation.
Benefits of Whole Foods for Insulin Regulation
Whole foods, such as vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that contribute to improved insulin sensitivity. These foods promote a slower, more stable glycemic response, reducing the need for excessive insulin secretion and helping to maintain natural insulin regulation.
Identifying Foods that Naturally Regulate Insulin
Foods that naturally regulate insulin include those with a low glycemic index (GI), such as non-starchy vegetables, most fruits, legumes, and whole grains. These foods cause a gradual rise in blood glucose and insulin levels. Additionally, foods rich in magnesium, chromium, and omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and support healthy insulin production.
The Glycemic Index and Insulin Response
Understanding the Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) is a valuable tool for understanding how different foods affect blood sugar levels. It ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how quickly and how much they raise blood sugar levels after consumption. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to a swift and significant rise in blood sugar. Conversely, low-GI foods are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual increase in blood sugar. This index is crucial for managing insulin response and maintaining hormonal balance, particularly for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Low-GI Foods and Their Role in Hormonal Balance
Low-GI foods play a pivotal role in hormonal balance by providing a steady source of energy and preventing sharp spikes in insulin levels. Foods such as whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and some fruits fall into this category. Incorporating these foods into the diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance. This is particularly important for individuals looking to manage or prevent type 2 diabetes and other related health conditions.
High-GI Foods and the Risk of Insulin Spikes
On the other end of the spectrum, high-GI foods can pose risks to insulin regulation. Foods such as white bread, sugary cereals, and processed snacks can cause rapid increases in blood sugar and insulin levels, known as insulin spikes. Frequent consumption of high-GI foods can lead to cells becoming less responsive to insulin, a condition known as insulin resistance. Over time, this can strain the pancreas, potentially leading to prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. Therefore, it is advisable to limit the intake of high-GI foods and opt for lower-GI alternatives to support hormonal health.
In conclusion, understanding and utilizing the glycemic index can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that support insulin production and hormonal balance. By choosing low-GI foods and limiting high-GI foods, one can manage insulin response effectively and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
Plant-Based Diets and Hormonal Health
Advantages of Plant-Based Diets for Insulin Sensitivity
Adopting a plant-based diet can have a profound impact on insulin sensitivity, a key factor in the management of diabetes and overall metabolic health. Studies have shown that diets rich in plant-derived foods can improve blood parameters, leading to lower insulin resistance and a reduced risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. The high fiber content and low glycemic load of plant-based foods contribute to a more stable blood sugar level, preventing the sharp spikes in insulin that are common with the consumption of high-glycemic foods. Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory properties of many plant foods may improve insulin sensitivity by reducing systemic inflammation, which is known to contribute to insulin resistance.
Key Nutrients in a Plant-Based Diet for Hormonal Regulation
While plant-based diets are associated with numerous health benefits, it is essential to ensure that they are well-balanced to avoid nutritional deficiencies that could affect hormonal health. Key nutrients that play a role in hormonal regulation include protein, B vitamins, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. Plant-based sources of these nutrients include legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens. For instance, legumes are an excellent source of protein and iron, while seeds like flax and chia are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Ensuring a diverse and nutrient-rich plant-based diet is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and overall health.
Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet should be a gradual and well-planned process to ensure it meets all nutritional needs and promotes hormonal health. Starting with small changes, such as incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into meals, can make the transition easier. It is also beneficial to seek guidance from a nutritionist or dietitian who can provide personalized advice based on individual health goals and nutritional requirements. Additionally, monitoring and adjusting the diet as needed can help prevent deficiencies and ensure that the diet continues to support hormonal balance and overall well-being.
In conclusion, a well-planned plant-based diet can offer significant advantages for insulin sensitivity and hormonal health. By focusing on nutrient-rich plant foods and ensuring a balanced intake of essential vitamins and minerals, individuals can harness the power of their diet to support hormonal function and reduce the risk of metabolic diseases.
Supplements and Natural Remedies for Insulin Control
Herbal Supplements and Their Impact on Insulin
Herbal supplements have been used for centuries to support various aspects of health, including blood sugar regulation. Fenugreek, for instance, contains soluble fiber that can slow down carbohydrate digestion and absorption, potentially leading to improved insulin sensitivity. Cinnamon is another popular herb that has been shown to mimic insulin activity and increase glucose uptake by cells. Additionally, berberine, found in plants like goldenseal, has been reported to improve insulin action and promote glucose metabolism.
The Role of Minerals and Vitamins in Insulin Production
Minerals and vitamins play crucial roles in the body’s ability to produce and regulate insulin. Magnesium is a mineral that is essential for insulin receptor function and has been linked to improved insulin sensitivity. Chromium is another mineral that enhances the action of insulin and is involved in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Vitamins such as Vitamin D and Vitamin B3 (niacin) have also been associated with insulin regulation, with deficiencies in these vitamins potentially leading to impaired insulin action.
Natural Remedies and Their Scientific Backing
Natural remedies, including lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments, can significantly influence insulin production and sensitivity. Regular physical activity is known to enhance insulin sensitivity and promote glucose uptake by muscle cells. Stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and yoga, may help lower cortisol levels, which in turn can improve insulin sensitivity. Adequate sleep is also essential, as sleep deprivation can lead to increased insulin resistance. Incorporating foods high in soluble fiber and adopting a plant-based diet can further aid in managing insulin levels naturally.
While these natural remedies and supplements show promise, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into your regimen, especially if you are currently on medication for blood sugar control. Scientific evidence supports the use of these interventions as part of a comprehensive approach to managing insulin levels and overall metabolic health.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Insulin Production
The Significance of Exercise in Insulin Management
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone in the management of insulin levels. Exercise enhances the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which means that cells are better able to use available insulin to take up glucose during and after activity. When muscles contract during exercise, they become more sensitive to insulin, allowing these cells to use glucose more effectively for up to 48 hours post-exercise. Regular activity also helps to maintain a healthy weight, which further improves insulin sensitivity and production. A combination of aerobic exercises, such as walking or swimming, and resistance training, like weight lifting, is most beneficial for overall insulin management.
Stress and Its Effect on Hormonal Balance
Chronic stress has a profound impact on hormonal balance, including the regulation of insulin. The body’s stress response triggers the release of various hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can lead to increased blood glucose levels. Over time, chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance, as the body’s cells become less sensitive to insulin’s effects. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and supporting insulin function.
Sleep Patterns and Insulin Sensitivity
Sleep plays a pivotal role in regulating insulin sensitivity. Disruptions in sleep patterns, such as those caused by sleep apnea or insomnia, can lead to decreased insulin sensitivity and increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes. Adequate, restful sleep helps to regulate the hormones that influence appetite and insulin release. Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support healthy insulin function. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime can improve sleep quality and, in turn, insulin sensitivity.
In conclusion, lifestyle factors such as exercise, stress management, and sleep have significant effects on insulin production and sensitivity. By incorporating regular physical activity, employing stress reduction techniques, and prioritizing sleep, individuals can empower their health and improve their hormonal balance, potentially reducing the risk of insulin-related health issues.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Health Through Diet and Lifestyle
Summarizing the Link Between Diet and Insulin
The intricate dance between diet and insulin production is a testament to the body’s remarkable ability to maintain balance. The foods we consume have a direct impact on insulin levels, with macronutrients like carbohydrates playing a pivotal role in insulin secretion. Diets high in processed foods and sugars can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, necessitating higher levels of this hormone for glucose uptake. Conversely, whole foods rich in fiber and nutrients support insulin sensitivity and natural regulation, underscoring the importance of dietary choices in hormonal health.
Practical Tips for Managing Insulin Naturally
- Balance Macronutrients: Aim for a diet that balances carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to prevent insulin spikes.
- Choose Low-GI Foods: Incorporate low glycemic index foods that slowly release glucose into the bloodstream.
- Increase Dietary Fiber: Consume plenty of fiber-rich foods like vegetables, legumes, and whole grains to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to enhance insulin uptake and glucose metabolism.
- Stress Management: Adopt stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga to prevent cortisol-induced insulin resistance.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure sufficient sleep as disrupted patterns can affect insulin sensitivity.
Encouragement for Continued Education and Self-Care
Understanding the relationship between diet and insulin is just the beginning. Continuous education on nutritional science and self-care practices is essential for long-term health. Empower yourself by staying informed about the latest research, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, and listening to your body’s unique needs. Remember, managing insulin naturally is not only about dietary adjustments but also about embracing a lifestyle that supports overall well-being. Take proactive steps towards your health, and let your food be the medicine that keeps your hormones in harmony.
Purium’s Super Life Formula
Contains a variety of herbs and plant extracts that have been proven to help increase muscle mass, normalize hormone levels, build endurance, speed muscle recovery, and increase libido.
Sources:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22601-insulin
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/insulinotropic#:~:text=In%20subject%20area%3A%20Chemistry,of%20insulin%20in%20the%20body.
https://www.diabetes.org.uk/guide-to-diabetes/enjoy-food/carbohydrates-and-diabetes/glycaemic-index-and-diabetes
https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/blood-glucose-and-exercise#:~:text=Physical%20activity%20can%20lower%20your,see%20the%20benefits%20of%20activity.