Sleep apnea is a common yet serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, known as apneas, can significantly affect a person’s quality of sleep and overall health. This article provides an in-depth exploration of sleep apnea, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and recommended lifestyle changes.
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea occurs when the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, reducing or stopping airflow. This can lead to reduced oxygen levels in the blood and fragmented sleep. There are three main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA):
- The most common form, caused by physical blockages of the airway, such as relaxed throat muscles or excess tissue.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA):
- Occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles responsible for breathing.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome:
- A combination of obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
The causes of sleep apnea vary depending on the type but often include the following:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea Causes:
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to fatty deposits around the neck, narrowing the airway.
- Anatomy: Structural issues such as a large tongue, tonsils, or uvula, and a small jaw can block airflow.
- Age: Muscle tone naturally decreases with age, increasing the risk of airway collapse.
- Family History: Genetic predispositions to narrow airways or other risk factors.
- Central Sleep Apnea Causes:
- Medical Conditions: Heart failure, stroke, or neurological diseases.
- Medications: Certain sedatives and pain medications can disrupt normal breathing signals.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea symptoms can range from mild to severe and often go unnoticed by the individual. Common symptoms include:
- Loud Snoring: A hallmark sign of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Pauses in Breathing: Observed by a bed partner.
- Gasping or Choking During Sleep: Results from attempts to resume breathing.
- Daytime Fatigue: Due to poor-quality sleep.
- Morning Headaches: Caused by low oxygen levels during sleep.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Cognitive impairment due to sleep disruption.
- Mood Changes: Irritability, depression, or anxiety.
Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
Diagnosing sleep apnea requires a thorough medical evaluation. Key steps include:
- Medical History and Physical Exam:
- A detailed review of symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
- Examination of the throat, neck, and nasal passages.
- Sleep Studies:
- Polysomnography (PSG): Conducted in a sleep lab, this comprehensive test measures brain waves, oxygen levels, heart rate, and breathing patterns.
- Home Sleep Apnea Testing (HSAT): A simplified test for detecting obstructive sleep apnea, performed at home.
- Additional Tests:
- Blood tests or imaging studies may be required to identify underlying conditions.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
Treatment for sleep apnea aims to restore normal breathing during sleep and improve overall health. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Common options include:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight loss and regular exercise can reduce airway obstruction.
- Avoiding alcohol, smoking, and sedatives that relax throat muscles.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP):
- A CPAP machine delivers a steady stream of air through a mask, keeping the airway open during sleep. It is the most effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea.
- Oral Appliances:
- Custom-made devices worn during sleep to reposition the jaw or tongue and keep the airway open.
- Surgery:
- In cases where other treatments are ineffective, surgical options include removing excess tissue, correcting structural abnormalities, or implanting devices to stimulate breathing.
- Treatment for Central Sleep Apnea:
- Addressing the underlying medical condition or using adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV) devices that regulate breathing.
Purium Products that can help with quality sleep:
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Sleep Apnea
Lifestyle adjustments play a critical role in managing sleep apnea and improving overall health. Key changes include:
- Weight Management:
- Losing weight can significantly reduce symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea by decreasing the fat deposits around the neck and airway.
- Sleep Positioning:
- Sleeping on the side instead of the back can prevent the tongue and soft tissues from blocking the airway.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives:
- These substances relax throat muscles, increasing the risk of airway collapse.
- Healthy Sleep Habits:
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a sleep-friendly environment can enhance the quality of sleep.
- Exercise:
- Regular physical activity improves overall respiratory function and reduces the severity of symptoms.
- Quitting Smoking:
- Smoking inflames and narrows the airway, exacerbating sleep apnea symptoms.
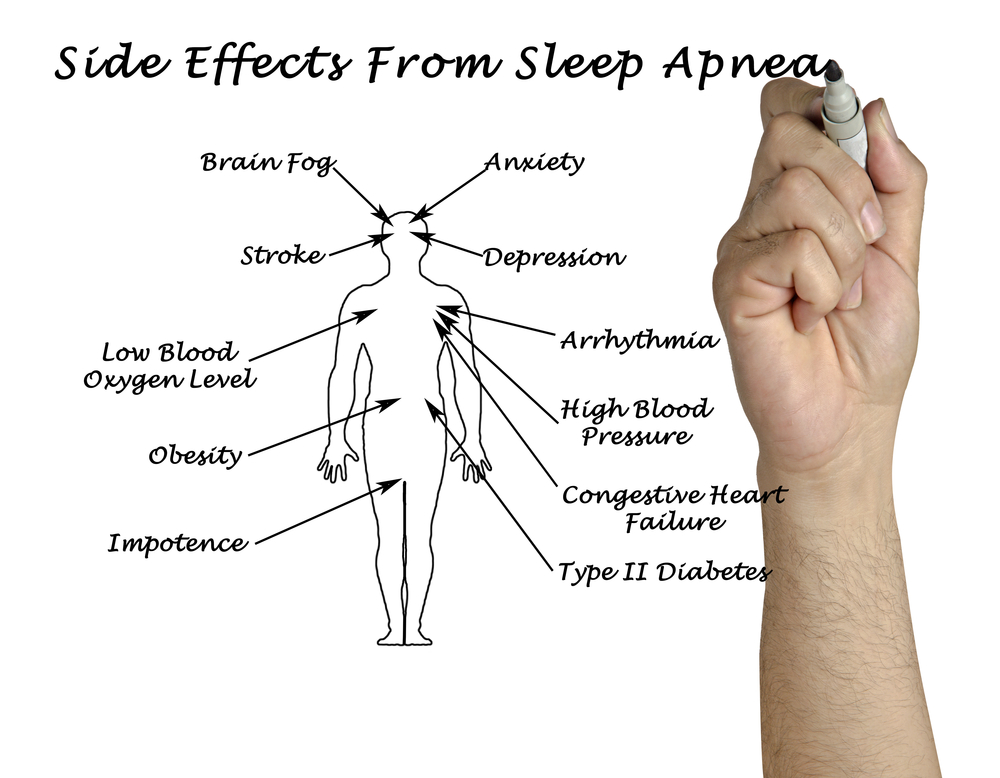
Complications of Untreated Sleep Apnea
If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Problems: High blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Increased risk due to insulin resistance.
- Daytime Accidents: Fatigue-related accidents and injuries.
- Cognitive Decline: Memory and concentration issues.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Due to chronic fatigue and mood disturbances.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a prevalent but manageable condition that requires timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. By addressing underlying causes, adhering to prescribed therapies, and making lifestyle changes, individuals with sleep apnea can significantly improve their health and quality of life. If you suspect you or a loved one may have sleep apnea, consult a healthcare provider to explore diagnostic and treatment options.
Sources:
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/sleep-apnea
https://aasm.org/aasm-releases-position-statement-home-sleep-apnea-testing/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/obstructive-sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20352090